Explaining Differences in Interest Rate Parity
There are different interest rate parity equations for covered and uncovered IRP. Why Interest Rate Parity Matters.
Heres the uncovered interest rate parity formula.

. It suggests that the difference between the forward exchange rate and spot exchange rates of two countries after a specific amount of time depends on the interest rates in the two countries. However exchange rates are determined by several other factors and not just. Covered IRP shows the forward exchange rate.
This theory argues that the difference between the risk free interest rates offered for different kinds of currencies. Define interest rate parity IRP and explain with US and India example when IRP does not hold good how the opportunities for covered interest arbitrage arise. If the interest rate differential i home i foreign exceeds the forward premium from the home country here the USA perspective there will be an inflow of funds into the home country.
The interest rate parity is a theory that suggests a link between the interest rates in two countries and the difference between the spot rate and forward rate of the currencies of the two countries. The fact that this condition does not always hold allows for potential opportunities to earn riskless profits from covered interest arbitrageTwo assumptions central to interest rate parity are capital mobility and. In particular the low interest rate currency should be expected to appreciate so much as to render an investor indifferent between 1 investing in the domestic.
Assumes that the actions of international investorsmotivated by cross-country differences in rates of return on comparable assetsinduce changes in the spot exchange rate. CIRP holds that the difference in interest rates should equal the forward and spot exchange rates. Uncovered interest rate parity exists when there are no contracts relating to the forward interest rate.
The current rate of interest in the US is 6. How should the amount of interest to be capitalized be determined. With covered interest parity there is a contract in place locking in the forward.
Please define the Interest Rate Parity Theorem and explain the equation which describes it. The interest rate parity theory A theory of exchange rate determination based on investor motivations in which equilibrium is. The interest rate parity theory A theory of exchange rate determination based on investor motivations in which equilibrium is described by the interest rate parity condition.
It is also known as the asset approach to exchange rate determination. Put simply the interest rate parity suggests a relationship between interest rates spot exchange rates and forward exchange rateswhich means investors can. Instead parity is simply based on the expected spot rate.
Assumes that the actions of international investorsmotivated by cross-country differences in rates of return on comparable assetsinduce changes in the spot exchange rate. Interest rate parity IRP is a concept which states that the interest rate differential between two countries is the same as the differential between the forwarding exchange rate and the spot exchange rate. In another vein IRP.
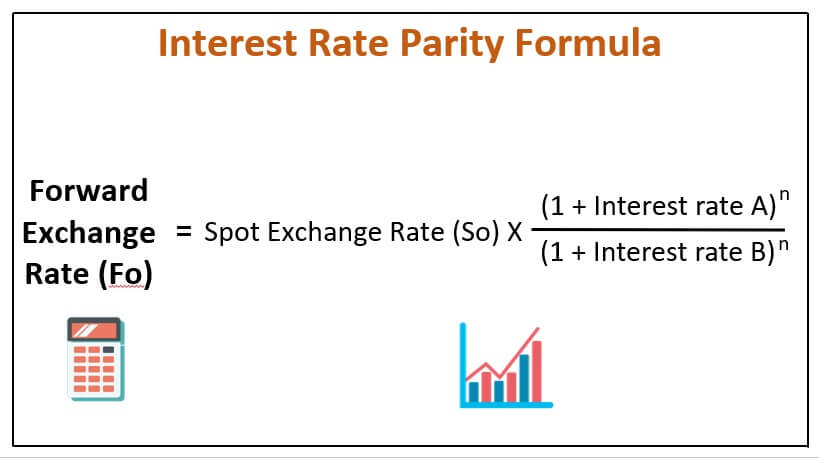
When discussing foreign exchange rates you may often hear about uncovered and covered interest rate parity. Forward Exchange Rate Fo Spot Exchange Rate So X 1 Interest rate An 1 Interest rate Bn The equation explains that the forward exchange rate Fo should equal the spot exchange rate So multiplied by the interest rate of country A home country divided by the interest rate of the country B foreign country. Interest rate parity is a no-arbitrage condition representing an equilibrium state under which investors interest rates available on bank deposits in two countries.
Assumes that the actions of international investorsmotivated by cross-country differences in rates of return on comparable assetsinduce changes in the spot exchange rate. It can be used to predict the movement of exchange rates between two currencies when the risk-free interest rates of the two currencies are known. Without interest rate parity banks could exploit differences in currency rates to make easy money.
What is the difference between the stated interest rate and the market. If the interest rate differential is less than the forward premium there would be outflow of investment funds from the home country. The interest rate parity theory A theory of exchange rate determination based on investor motivations in which equilibrium is described by the interest rate parity condition.
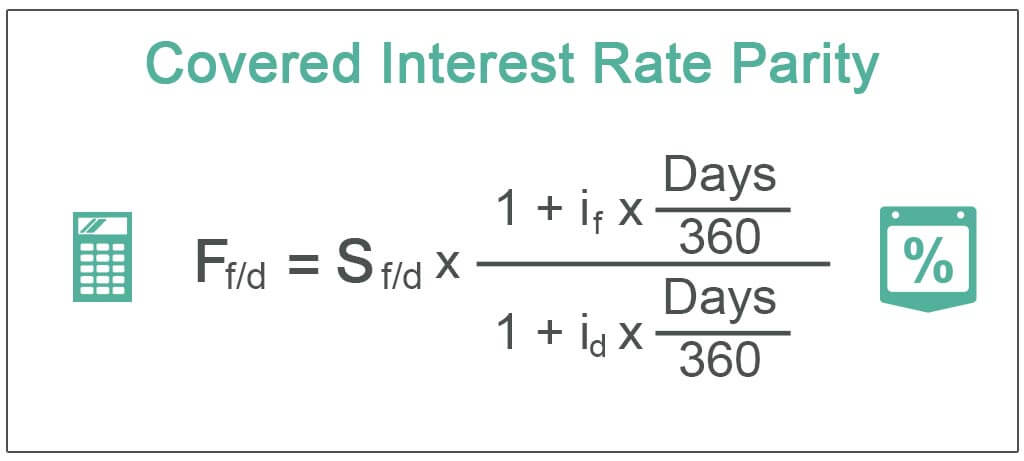
Ftab Stab 1 iaT 1 ibT. In another vein IRP. Covered interest rate parity CIRP is a theoretical financial condition that defines the relationship between interest rates and the spot and forward currency rates of two countries.
Interest rate parity IRP A condition in which the rates of return on comparable assets in two countries are equal. Uncovered IRP shows the spot exchange rate. Uncovered interest rate parity UIP states that the difference in two countries interest rates is equal to the expected changes between the.
Without interest rate parity it would be very easy for banks and investors to exploit. The uncovered interest rate parity UIRP is a no-arbitrage principle that suggests that any interest rate differential between two countries should be completely offset by an adverse movement in the exchange rate. The investor invests US 100 in his country at the present interest rate of 6.
The interest rate parity theory is a powerful idea with real implications. Uncovered interest rate parity UIP theory states that the difference in interest rates between two countries will equal the relative change in currency foreign exchange rates over the same period. STab Stab 1 ia 1 ib The covered interest rate parity formula looks like this.
FR 08 x 1 04 1 x 106 08 x 104 1 x 106 0785. The interest rate parity theory A theory of exchange rate determination based on investor motivations in which equilibrium is described by the interest rate parity condition. Despite foreign currency transaction exposure there does not seem to be in.
Is a theory used to explain the value and movements of exchange rates. The theory of interest rate parity is based on the notion that the returns on an investment are risk-free In other words in the examples above investors are guaranteed 3 or 5 returns. The profit loss arises mainly on exchange difference in repayment of foreign currency loan.
Interest rate parity theory assumes that differences in interest rates between two currencies induce readjustment of exchange rate. In both cases here are. What interest rates should be used in determining the amount of interest to be capitalized.
We can calculate the forward exchange rate ratio with the help of the difference in the rates of interest as follows. In another vein IRP.
Covered Interest Rate Parity Cirp Definition Formula Example
Interest Rate Parity Irp Definition
Interest Rate Parity Definition Formula How To Calculate

Interest Rate Parity Meaning Application Types And Equilibrium Rate

No comments for "Explaining Differences in Interest Rate Parity"
Post a Comment